Apple Patches Two Exploited Vulnerabilities
Apple fixed two vulnerabilities that are, according to Apple, already being exploited. The WebKit vulnerability could be used by a malicious website to execute arbitrary code, while the Kernel issue can then be used to escalate privileges. No additional details are known at this point.
| MacOS Monterey | iOS/iPadOS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2022-32894 [important] Kernel An out-of-bounds write issue was addressed with improved bounds checking. An application may be able to execute arbitrary code with kernel privileges. Apple is aware of a report that this issue may have been actively exploited. |
|||||||
| x | x | ||||||
| WebKit Bugzilla [critical] WebKit An out-of-bounds write issue was addressed with improved bounds checking. Processing maliciously crafted web content may lead to arbitrary code execution. Apple is aware of a report that this issue may have been actively exploited. |
|||||||
| x | x | ||||||
---
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS.edu
Twitter|
A Quick VoIP Experiment
To better detect any exploit attempts taking advantage of the recent Realtek vulnerability, I experimented with the open source VoIP server Asterisk. I just set it up, listening for inbound connections. The server had no existing accounts configured or connected to an upstream VoIP service. Using it for actual phone calls was impossible, but it would respond.
Even without exposing a VoIP service, there is always a trickle of SIP traffic, probing if something is listening. Here is a random packet from my home network:
INVITE sip:0011972567100000@[redacted] SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 62.210.6.91:4040;branch=zgwRH80hCA
Max-Forwards: 70
From: <sip:[redacted]@[redacted]>;tag=159263
To: <sip:0011972567100000@[redacted]>
Call-ID: zgwRH80hCA0fUGY
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Contact: <sip:[redacted]@62.210.6.91:4040>
Expires: 3600
Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, OPTIONS, BYE, REFER, NOTIFY, MESSAGE, SUBSCRIBE, INFO
User-Agent: Gigaset N670 IP PRO/83.V2.23.0
Content-Type: application/sdp
Content-Length: 180
v=0
o=8001 16264 18299 IN IP4 0.0.0.0
s=SIP Call
c=IN IP4 0.0.0.0
t=0 0
m=audio 25282 RTP/AVP 0 101
a=rtpmap:0 pcmu/8000
a=rtpmap:101 telephone-event/8000
a=fmtp:101 0-11
This appears to be an attacker at 62.210.6.91 attempting to call a number in Israel."5", the digit following the country code, should indicate that this is a mobile number according to Wikipedia, with 56 being used in the Palestinian territories. But it may very well be that automated scripts use non-existing numbers and the standard responses for non-existing numbers to determine if a specific SIP server can be used.
Once I set up the Asterisk server, the attempts to connect immediately exploded (this is data from a /24):
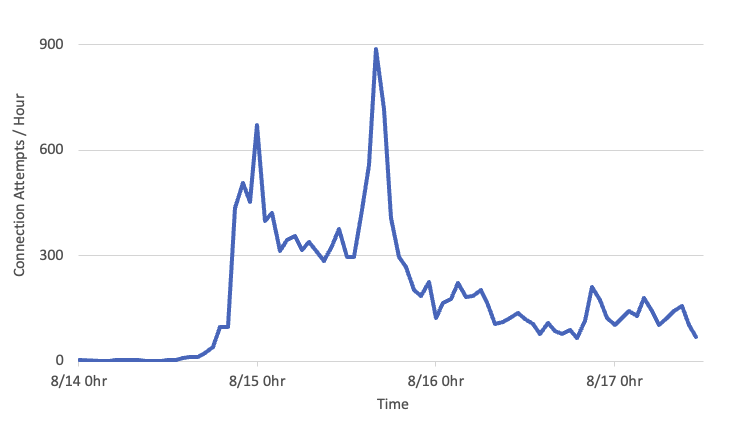
I was experimenting with the setup, which may explain the decrease after the first spike. These logs are also "sampled," so the number of connections was much higher.
The main attack I observed was brute forcing attempts. As I didn't set up an upstream provider, all calls were considered "local" by the server. A request like the above would result in an "extension not found" error. Throughout this experiment, I received 77,610 requests (about two days' worth of data).
The most dialed number was +1 (708) 838 2179. A number in Chicago, but a quick Google search didn't return anything significant. The second most common number dialed was +972 59 5144330, another number in the Palestinian territories.
In addition, we had 28 Million(!) attempts to log in to connect an extension to our VoIP server. The most used extensions were 100, 101, 10, 200, and 1000. All extensions are often the first ones registered.
There is no big and exciting lesson here. But the number of attacks you see may depend on what services you expose, and a SIP server appears to attract the scans like [insert witty analogy here].
---
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS.edu
Twitter|


Comments